On Wednesday, March 13, 2024, the European Parliament approved the Artificial Intelligence Act, a significant piece of legislation aimed at ensuring the safety and compliance of AI systems with fundamental rights, while also fostering innovation within the European Union.
This act is considered the world’s first major regulatory framework specifically designed to govern artificial intelligence.
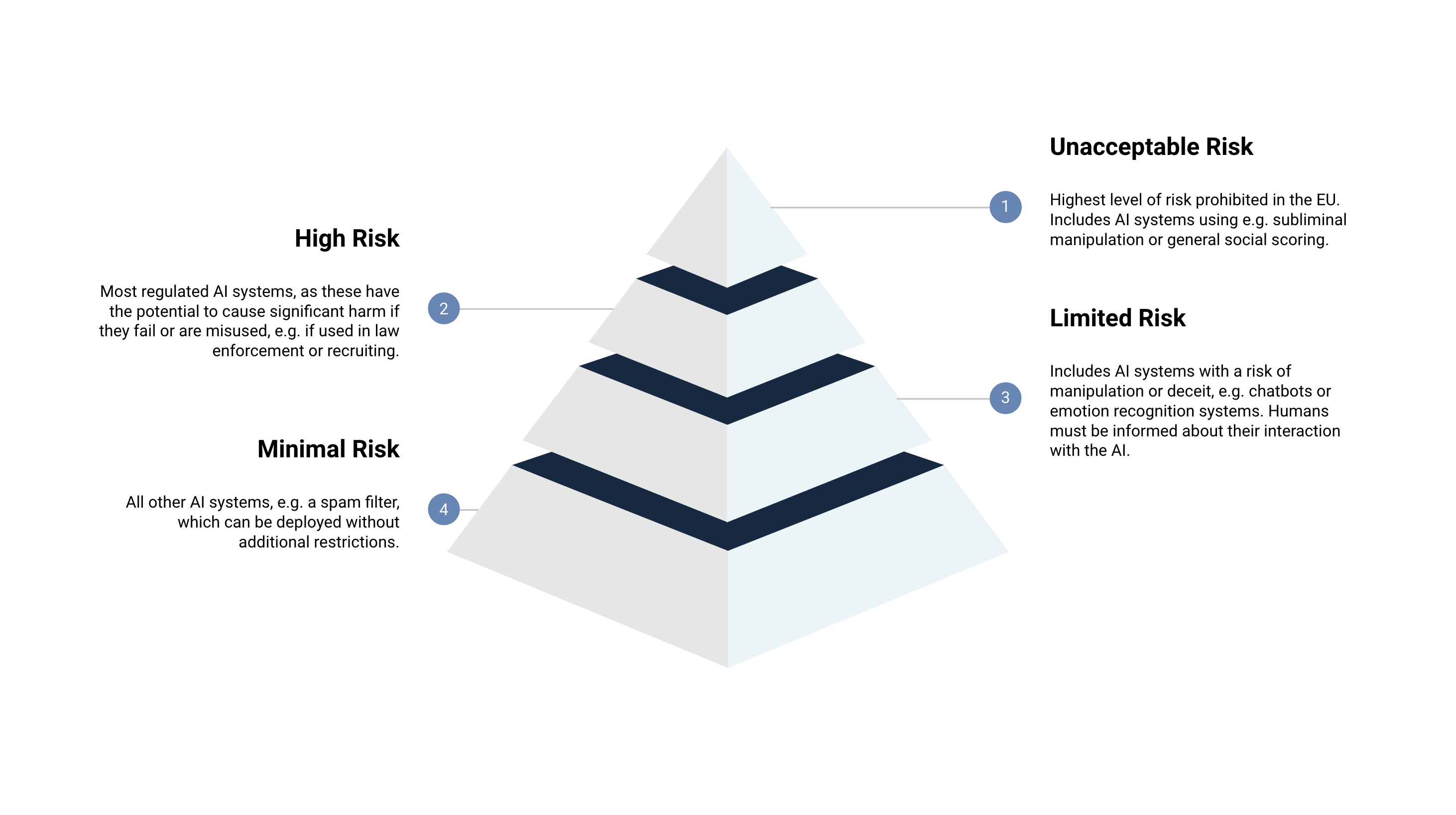
The AI Act categorizes AI technologies based on their level of risk, ranging from “unacceptable” to high, medium, and low hazard. Technologies deemed “unacceptable” will be banned, while high-risk AI systems will face stringent obligations.
The regulation is expected to enter into force at the end of the legislative term in May, after final checks and endorsement from the European Council, with staggered implementation starting from 2025.
Key provisions of the AI Act include:
- Bans on prohibited practices, effective six months after the law comes into force.
- Codes of practice to be established nine months after the law comes into force.
- Rules for general-purpose AI, including governance, to be implemented 12 months after the law comes into force.
- Obligations for high-risk systems to be applied 36 months after the law comes into force.
The act also introduces transparency requirements for general-purpose AI systems, mandates clear labeling of deepfakes, and establishes regulatory sandboxes for innovation and support for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
The AI Act is a direct response to citizens’ proposals from the Conference on the Future of Europe (COFE), addressing the need for a safe and trustworthy society, human oversight of AI, and improved access to information for citizens, including those with disabilities.
The law will be fully applicable 24 months after its entry into force, with specific provisions for general-purpose AI, biometric identification systems, social scoring bans, and consumer rights to launch complaints and receive explanations.
The European Parliament’s approval of the AI Act marks a significant step in the regulation of AI, setting a precedent for other countries to follow and addressing the balance between innovation and the protection of citizens’ rights.